-
What You See is
What You TreatRadiopharmaceuticals are drugs that contain radioactive isotopes and are used for diagnosis or therapy. Their mechanism of action depends on their intended use:
For diagnosis: Radiopharmaceuticals are designed to target specific organs, tissues, or cellular receptors. Once administered into the body, they emit radiation (usually gamma rays or positrons) that can be detected by imaging devices such as PET or SPECT scanners. This allows doctors to visualize physiological processes and detect abnormalities like tumors or organ dysfunction.
For therapy: Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals deliver targeted radiation (often alpha or beta particles) directly to diseased cells, such as cancer cells. The radiation damages the DNA of these cells, leading to their destruction while minimizing harm to surrounding healthy tissues.
The effectiveness of radiopharmaceuticals lies in their ability to combine targeting molecules (such as peptides, antibodies, or small molecules) with radioactive isotopes, achieving precise diagnosis and treatment at the molecular level.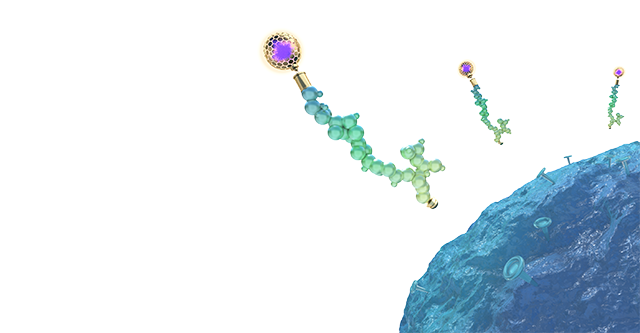
What are the advantages of our technology platform?
-
RDC Linker Optimization Platform
The proprietary radiopharmaceutical linker technology platform developed by Norroy Bioscience is specifically designed for radiopharmaceutical applications. It enables efficient and stable conjugation between radioactive isotopes and targeting ligands such as peptides, antibodies, or small molecules. The linker structure has been optimized to ensure the radionuclide remains securely bound during systemic circulation, thereby reducing radiation exposure to non-target tissues and improving overall drug safety. Additionally, it can modulate the affinity and biodistribution of the compound, ultimately influencing both the efficacy and safety profile of the radiopharmaceutical.
-
Rapid Translational Medicine Technology Platform
An advanced drug development tool designed to accelerate the discovery and development of novel radiopharmaceuticals in nuclear medicine. This platform harnesses high-throughput screening technology, utilizing automation and informatics to rapidly and accurately assess the activity of large compound libraries, identifying radiopharmaceutical candidates with potential clinical value. It further enables in vivo validation of drug-like properties, establishing an efficient evaluation system.




